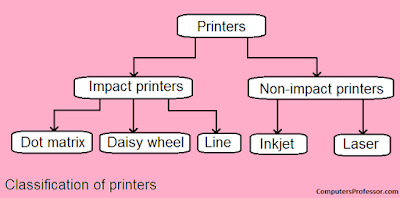
These printers print characters by
striking an inked ribbon against the paper.
Advantages
·
These
printers enable the user to produce carbon copies.
·
They
are cheap.
Disadvantages
·
Impact
printers are slow.
·
They
offer poor print quality, especially in the case of graphics.
·
They
can be extremely noisy.
·
They
can print only using the standard font.
Non-Impact
Printers
These
are much quieter than impact printers, as their printing heads do not strike
the paper. They offer better print quality, faster printing, and the ability
to create prints that contain sophisticated graphics.
Advantages
· Non-impact
printers produce prints of good quality, and hence render sophisticated
graphics.
· They
are noiseless.
· They
are fast.
· They
can print text in different fonts.
Disadvantages
·
These
printers are expensive.
·
The
ink cartridges used by them are also costly.
Dot
Matrix Printer
A dot matrix printer prints characters and images off
all types as a pattern of dots (hence the name). This printer has a print
head (or hammer) that consists of pins representing the character or image.
The print head runs back and forth, or in an up-and-down motion on the page
and prints by striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the paper. The
speed of dot matrix printers varies in the range of 50–500 cps (character per
second).
Advantages
· The
dot matrix printer can produce carbon copies.
· It
offers the lowest printing cost per page.
· It
is widely used for bulb printing where the quality of the print is not of
much importance.
· It
is cheap.
· When
the ink is about to be exhausted, the printout gradually fades rather than
suddenly stopping partway through a job.
· It
can used continuous paper rather than individual sheets, making them useful
for data logging.
Disadvantages
· This
type of printer creates a lot of noise when the pins strike the ribbon
against the paper.
· It
can only print lower resolution graphics, with limited quality.
· It
is very slow.
· It
has poor print quality.
Daisy
Wheel Printer
A daisy wheel printer uses an impact
printing technology to generate high-quality output comparable to
typewriters, and is three times faster. The key benefit of using a daisy
wheel printer is that the print quality is high, as the exact shape of the
character hits the ribbon to leave an impression on the paper.
Line
Printer
A line printer is a high-speed
impact printer in which one typed line is printed at a time. The speed of a
line printer usually varies from 600 to 1200 lines per minute, or
approximately 10-20 pages per minute. Because of their high speed, line
printers are widely used in data centers and in industrial environments.
Band
Printer
A
band printer (loop printer), is an impact printer with a printing mechanism
that uses a metal loop or band to produce typed characters. The set of
characters are permanently embossed on the band, and this set cannot be
changed unless the band is replaced. The band itself revolves around hammers
that push the paper against the ribbon, allowing the desired character to be
produced on the paper.
The
main advantage of using a band printer is its high speed. This type of
printer can print 2,000 lines per minute, and it, therefore, perfect for high
volume printing in businesses, schools, and other organizations.
Inkjet
Printer
Inkjet
printers have made rapid technological advances in recent year. The print
head of inkjet printers have several tiny nozzles, also called jets. As the
paper moves past the print head, the nozzles spray ink onto it, forming
characters and images.
While
inkjet printers are cheaper than laser printers, they are more expensive to
maintain. The cartridges of inkjet printers have to be changed more
frequently, and the special coated paper required to produce high-quality
output is very expensive.
Laser
Printer
A laser printer, shown in is a
non-impact printer that works at very high speeds and produces high-quality
text and graphics. It uses the technology used in photocopier machines. When
a document is sent to the printer, the following steps take place :
· A
laser beam ‘draws’ the document on a drum (which is coated with a
photo-conductive material) using electrical charges.
· After
the drum is charged, it is rolled in a toner (a dry powder type of ink).
· The
toner sticks to the charged image on the drum.
· The
toner is transferred onto a piece of paper and fused to the paper with heat
and pressure.
· After
the document is printed, the electrical charge is removed from the drum and
the excess toner is collected.
|