Write about Pointers & Arrays.
https://www.computersprofessor.com/2016/06/write-about-pointers-arrays.html
When an arrays is declared, the compile allocated a base
address and sufficient amount of storage contain all the elements of an array in
contiguous memory locations.
® The base address, is the location of 1st
element (index 0) of the array.
®The compiler also defines the array
name as a constant pointer to the 1st
element.
®Suppose we declare a array x as
follows int x as follows.
int x[5] = {5, 9, 6, 3, 7};
Suppose the base address of x is 166 and assuming that
each integer requires 2 bytes;
If we declare ‘P’ as an integer pointer, then we can make
the pointer ‘p’ to point to the array x
by the following assignment.
p=x;
This is equivalent to p = &x[0];
Now, we can access every value of x using p++ to move
from one elements to other.
The relationship between p&x is shown below.
P=&x[0](=166)
P+1=&x[1] (=168)
P+2 = &x[2](=170)
P+3 = &x[3](=172)
P+4 = &x[4](=174)
You can
notice that the address of an element is calculated using its index and the scale
factor of the data.
Address of
x[3] = base add+(3´scale
factor of int)
= 166+3´2 = 172
®We can use pointers to access array
elements as:
*(P+3) gives value of x[3]
®The pointer accessing method is much
faster than array indexing.
Ex:–
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
int *p,
sum, i;
int x[5] = {5, 9, 6, 3, 7};
i=0;p=x;
while(i
{
printf(“x[%d]%d%u\n”,
i, *p, p);
sum=sum+*p;
i++,p++;
}
printf(“sum=%d\n”, sum);
getch();
}
Out Put:
element value address
x[0] 5 106
x[1] 9 108
x[2] 6 120
x[3] 3 172
x[4] 7 174
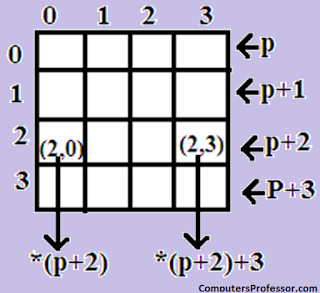
Manipulate Two Dimensional Arrays:
We known
that in a one Dimensional array x, the expression,
*(x+i) (or) *(p+i)
Represents the element x[i].
®Similarly a element, in a Two Dimensional array can be
represented by the pointer expression as follows.
*(*(p+i)+j) is equal to x[i][j].
Columns
p¬pointer
to 1st row.
p+i¬pointer
to ith row.
*(p+i) ¬pointer to 1st element In ithrow
*(p+i)+j¬pointer to jth element in ith
row
*(*(p+i)+j)¬value stored in the cell (i, j)
Pointers & Character Strings:–
Strings
are declared & initialized as follows:
char str[5] = “good”;
®The compile automatically inserts the
null characters ‘\0’ at the end of the string.
®’C’ supports an alternative method to
create strings using pointers variables of type char.
Ex:– char *str=”good”;
This
created a string for the literal and stores its address in the pointers
variable string.
®The pointer string now pointers to the
1st character of string ‘good’ as:
g
|
o
|
o
|
d
|
\0
|
We can
also use the run time assignment for giving values to a string pointer.
Ex:– char *str1;
str1=”good”; puts(str1);
str1 is
a pointer to the string, it is also the name of the string\, we do not need to use indirection
operator * here.
Ex:–
WAP to determine the length of a character string using
pointer.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
main()
{
char*name;
int len;
name = “DELHI”;
char *ptr=name;
while(*ptr!=’\0’)
{
printf(“%c is stored at address %u \n”,*ptr, ptr);
ptr++;
}
len=ptr–name;
printf(“length of the string is = %d\n”, len);
}
Out Put:
DELHI
D is stored at add
54
E is stored at add 55
L is stored at add 56
H is stored at add 57
I is stored at add 58
Length of the string is 5
Array of Pointers:
One imp.
Use of pointer is in handling of a table of strings consider the following
array of strings.
char
name[3][15];
This say that the name is a table containing 3 names,
each with a max length of 25 characters including null characters.
Ex:–
char*name[3]
={“New Zealand”, “Australia”, India”};
declares name to be an array of 3 pointers to characters,
each pointer pointing to a particular name as:
name[0]®New
Zealand
name[1]®Australia
name[2]®India
this declaration allocates only 28 bytes sufficient to
hold all the characters as shown:
|
The following statement would print out all the 3 names
for(i=0;i<=2;i++)
printf("%s\n",name[i]);
To access the jth character in the ith
name, we may write as:
*(name[i]+j)